You can get quality COPD Nursing Assignment Help from our professional tutors at Essay For All. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a widespread and preventable chronic disease. Generally, this disease has a close nexus with rapidly increasing physical, social, and economic burdens due to hospitalizations and healthcare costs. Health statistics show that approximately 210 million individuals globally suffer from this condition, and the cases continue to rise.
As a result, the disease will likely pose a global threat in the subsequent years. For this reason, prompt measures are necessary to curb its adversity. This condition entails respiratory airflow limitation that does not fluctuate significantly. The Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Diseases argues that COPD is both treatable and preventable. Furthermore, COPD is classified into the following two essential aspects:
- Chronic bronchitis is the first type of airway disease characterized by a cough and sputum production from a minimum of twelve weeks. Chronic bronchitis is synonymous with blue bloaters. In most cases, pollutants and allergies irritate the airway resulting in the production of sputum by the mucus-secreting cells and goblet cells.
- Emphysema is a pathogenic concept outlining an abnormal enlargement of the airspaces above the terminal bronchioles and damaging the alveoli walls. Whenever this happens, it results in impaired carbon dioxide and oxygen exchange. The situation destroys the alveoli walls.
The two can sometimes be confusing due to the overlapping symptoms that patients can have about them. As a result, differentiating them might prove challenging. In addition, we have two different emphysema types.
They are panlobular and centrilobular. The rising COPD potential and its potential as a health risk factor in the coming years make it imperative for nursing students to have adequate and relevant knowledge of this condition.
The pathophysiology and epidemiology of COPD
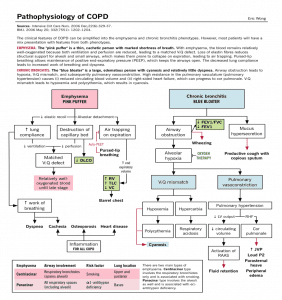
The primary underlying feature of COPD is that the airflow limitation is progressive and linked to abnormal inflammatory lung response to toxic gases and particles. COPD clinical features revolve around its classification. This insinuates that COPD pathophysiology is anchored on chronic bronchitis and emphysema classification.
In most cases, most patients manifest combined features of chronic bronchitis and emphysema. For COPD patients suffering from chronic bronchitis, airway obstructions result in hypoxia. Consequently, this results in pulmonary vasoconstriction. As a result, the high opposition in the pulmonary vasculature results in the following:
- Reduced blood circulation volume.
- The failure of the right side of a person’s heart.
On the other hand, in emphysema, a person’s blood remains adequately supplied with oxygen because of minimal ventilation and perfusion. This results in a matched V.Q defect. The loss of elastin fibers significantly reduces alveoli structural support.
Therefore, during expiration, alveoli easily collapse due to lack of support, resulting in trapping. Routinely, pursed-lip breathing maintains positive end-expiratory pressure, keeping the airways always open. So, lung compliance causes increased breathing and dyspnea. The figure below elaborates on this in detail.
Over the past years, COPD cases have continued to rise globally. In the United States, it is ranked as the fourth leading cause of death, with more than 125000 losing their lives annually because of this disease. This chronic obstructive pulmonary disease infection rate among women has increased since 2005.
Statistics show that the percentage of women succumbing to this disease is high than men. On average, about twelve million Americans have been diagnosed with this disease. The leading COPD causes include hosts and environmental factors. These include the following:
- Smoking, which severely depresses scavenger cell activities leading to respiratory tract infections.
- Genetic abnormalities due to enzyme inhibitors.
The role of nurses in COPD nursing
Mortality projections show that COPD will result in multiple deaths as the years’ progress. Nurses are part and parcel of every care setting and continue to play a crucial role in care provision for all chronic illnesses, including COPD. Like other infections, nurses participate in COPD management at every stage. For example, they are part and parcel of the strategies to mitigate the disease. Equally important, nurses also provide end-of-life care to COPD patients in different settings.
Some end-of-life care services are provided in the community, patient homes, and hospitals. In addition, they offer telemedicine care to patients, including COPD patients. Over the years, nurse-initiated intervention measures have allowed them to supplement or extend the services provided by doctors. Additionally, nurses undertake various activities to ascertain COPD patient conditions. These roles can be summarized below:
- Nurse-led consultations. Studies show that nurses play extensive roles in managing respiratory diseases. For this reason, they are involved in the long-term management of respiratory diseases. For example, nurses play a core role in asthma and COPD management. Studies have also affirmed that nurses complement the roles of doctors. As a result, they are pivotal in managing long-term respiratory diseases.
- Secondly, they take part in nurse-led management and intervention approaches. Generally, nurses offer holistic care toward managing various diseases. For COPD patients, nurses deliver non-pharmaceutical measures to mitigate symptoms and improve life quality. For instance, nurses can initiate smoking cessation intervention measures on patients to minimize the adversity of particular diseases and enhance their life quality.
- Finally, nurses’ roles of care remain core. They understand various illnesses and know better ways of curbing them. For this reason, nurses guide patients in every step to ensure their full recovery.
COPD management
The negative implications of COPD demand appropriate measures to curb its adverse effects. In most cases, medical management of this respiratory illness relies on health data assessment. Consequently, they define a suitable intervention to match the current manifestation. The commonly used approaches involve the following:
- Pharmacologic therapy through bronchodilators relieves a patient from bronchospasm since it interferes with the smooth muscle tone to minimize airway obstruction. This allows a high oxygen supply within the lungs to enhance alveoli ventilation.
- Management of exacerbations uses medications to facilitate bronchioles optimization by regularly ascertaining the most appropriate medications for patients. Experts can also use oxygen therapy to manage COPD.
- Finally, persons with this condition can also go for surgery to enhance how the lungs function.